Protein glycosylation is a key type of post-translational modification (PTM) that plays a vital role in numerous biological functions, including cell signaling, protein stability, immune response, and intercellular communication. Among them, N-glycosylation has become one of the most prominent topics in proteomics research due to its ubiquity and complexity. To accurately analyze the structure and functional characteristics of glycoproteins, it is often necessary to remove N-linked glycans from proteins to enable further study of both the protein and the released glycans. PNGase F (Peptide-N-Glycosidase F) is a highly efficient glycosidase that specifically removes high-mannose, hybrid, and complex N-linked oligosaccharides from glycoproteins, thereby facilitating subsequent analysis of the protein sample.
As a leading supplier of consumables for protein sample preparation, MtoZ Biolabs offers sequencing grade PNGase F with high purity, high activity, and excellent compatibility to meet the needs of scientific research and advance glycoprotein studies.
Product Overview
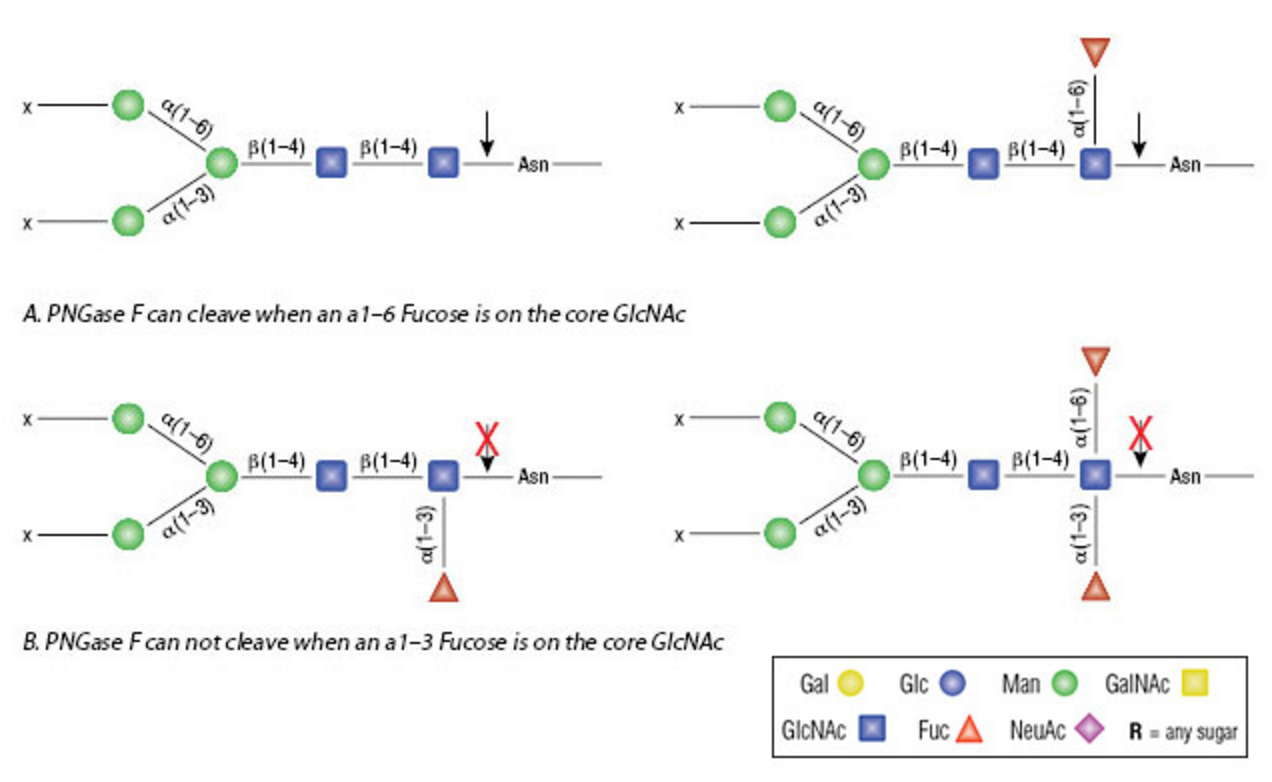
PNGase F (Peptide-N-Glycosidase F) is a specific amidase derived from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that specifically recognizes and efficiently cleaves the bond between the innermost N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and the asparagine (Asn) residue in N-linked glycoproteins. PNGase F can effectively remove high-mannose, hybrid, and complex types of N-linked oligosaccharides, releasing intact glycan structures without compromising their integrity, which significantly facilitates subsequent structural and functional analysis of glycans. As illustrated below, PNGase F can efficiently cleave glycans modified with core α1-6 fucose but cannot cleave those modified with core α1-3 fucose, demonstrating its high substrate specificity.
Source: Wikipedia
Figure 1. PNGase F Cleavage Site.
Product Details
Sequencing grade PNGase F undergoes rigorous quality control and contains no detectable endoglycosidase contaminants (Endoglycosidase F1, F2, F3) or other protease impurities. The purity exceeds 95%, as verified by SDS-PAGE and intact ESI-MS analysis.
|
Product Size |
50 µL,10 units/µL |
|
Buffer Composition |
20 mM Tris-HCl,pH=7.5,50 mM NaCl,5 mM EDTA |
|
Molecular Weight |
35 kDa |
|
Storage Conditions |
Store at 2-8 °C |
|
Optimal pH |
6.0-10,with an optimal pH of 8.6 |
|
Shelf Life |
12 months when stored at 2-8 °C |
Protocol
1. Recommended Digestion Conditions
Enzyme-to-substrate ratio (unit activity: μg protein): typically 2 μL enzyme: 20 μg protein, with a total reaction volume of 20 μL recommended.
Optimal pH: 8.6; Optimal temperature: 37 °C.
Digestion time: 4-18 hours, depending on the glycoprotein's structure and condition.
2. Reaction Termination Method
Terminate the reaction by lowering the temperature to below -20 °C or by adding SDS-PAGE sample buffer.
Features and Benefits
1. High Specificity
Specifically removes high-mannose, hybrid, and complex-type N-glycans without affecting O-linked glycans.
2. High Purity, Low Background
HPLC purity ≥99%, free of contaminating enzymes, ensuring precise and reliable experimental results.
3. Enzymatic Activity
40,000 units/min/mg.
4. Broad Experimental Compatibility
Suitable for use under both native and denaturing conditions; compatible with various sample types and workflows.
5. Complete Glycan Release
Releases intact glycan structures, ideal for downstream glycomics analysis and functional studies.
Applications
1. Glycoprotein Structure and Function Studies
Removal of N-glycans facilitates the investigation of how glycosylation affects protein function.
2. Proteomics Research
Eliminating glycan interference enhances the resolution and accuracy of mass spectrometry-based protein identification.
3. Biopharmaceutical Quality Control
Analyzing glycosylation heterogeneity helps evaluate drug stability, bioactivity, and immunogenicity.
4. Glycan Structure Analysis and Glycomics Research
Sequencing grade PNGase F provided by MtoZ Biolabs offers high purity, superior enzymatic efficiency, and excellent stability to support glycoprotein-related research. Its high specificity, exceptional cleanliness, and robust performance ensure accurate and reliable experimental outcomes. This enzyme is broadly applicable to glycoprotein structural analysis, protein mass spectrometry, biopharmaceutical development, and glycomics studies, making it an indispensable tool for glycoprotein research in the laboratory.
FAQs
Q1: Can Samples Treated with PNGase F Be Directly Used for Mass Spectrometry Analysis?
A1: Yes, samples treated with PNGase F are fully compatible with mass spectrometry analysis and require no additional complex processing steps.
Q2: Can PNGase F Remove All Types of Glycans?
A2: PNGase F specifically removes high-mannose, hybrid, and complex N-linked glycans. It does not cleave glycans containing core α1-3 fucose residues and is not suitable for removing O-linked glycans.
Q3: Why Is NP-40 Added When Using PNGase F?
A3: SDS inhibits the enzymatic activity of PNGase F. Adding the nonionic detergent NP-40 counteracts this inhibition, ensuring efficient enzymatic digestion.
Q4: How Can I Confirm Complete Deglycosylation?
A4: SDS-PAGE can be used to observe shifts in molecular weight as a preliminary confirmation. Mass spectrometry can provide a precise determination of glycan removal.
Q5: What Is the Difference between PNGase F and Endo-H?
A5: PNGase F has broad substrate specificity and removes nearly all N-linked glycans (except those with core α1-3 fucose), whereas Endo-H only removes high-mannose and some hybrid-type glycans.
Q6: What Types of Samples Are Suitable for PNGase F Digestion?
A6: PNGase F is suitable for various glycoprotein samples, including cell lysates, serum/plasma, recombinant proteins, and immunoprecipitated materials.













