Proteomics is a powerful approach for systematically studying protein species, expression levels, functional states, and regulatory networks, playing a pivotal role in disease mechanism research, drug development, and precision medicine. In serum proteomics research, high-abundance proteins (such as albumin and immunoglobulin G (IgG)) typically account for more than 80% of the total protein mass, severely masking the detection signals of low-abundance proteins and limiting the sensitivity and coverage of downstream analyses like mass spectrometry.
Traditional methods for removing high-abundance proteins often suffer from low depletion efficiency, significant sample loss, labor-intensive workflows, and poor reproducibility, making them unsuitable for high-throughput and high-precision studies. The abundant serum protein depletion kit from MtoZ Biolabs employs magnetic nanoparticle-based enrichment technology to efficiently and selectively remove multiple interfering high-abundance proteins while preserving the integrity of low-abundance targets. This enables reliable sample pretreatment for clinical research, biomarker discovery, and disease mechanism studies.
Product Overview
The abundant serum protein depletion kit from MtoZ Biolabs is specifically designed for serum protein samples, which utilizes advanced magnetic nanoparticle technology to selectively remove multiple high-abundance proteins, thereby significantly enhancing the detection of low-abundance proteins and providing clearer, more comprehensive data support for proteomics research. The kit is applicable to serum samples derived from humans as well as various animal species, and it is fully compatible with a wide range of downstream analytical techniques, including but not limited to LC-MS/MS, SDS-PAGE, Western Blot, and ELISA. It serves as an ideal solution for applications such as disease mechanism studies, biomarker discovery, and clinical sample analysis.
Product Notes
1. Lysis Buffer 1 should be freshly prepared before use by mixing Lysis Buffer A and B components.
2. Once sample preparation is completed, use immediately or aliquot and store at -80°C.
3. The abundant serum protein depletion kit is capable of processing 8 samples.
4. Avoid foam formation during operation to prevent interference with protein binding efficiency.
5. It is recommended to use low protein-binding centrifuge tubes to collect the eluted solution in order to minimize sample loss due to low-abundance protein adhesion to the tube walls.
6. Since protein concentrations in serum samples may vary between batches, it is advised to perform a preliminary test to determine the optimal dilution ratio and incubation time.
Product Details
|
Product Details |
Size |
Storage Conditions |
|
Wash buffer 1 |
2 mL×1 |
RT |
|
Wash buffer 2 |
8 mL×1 |
RT |
|
Lysis buffer A |
3.75 mg×1 |
RT |
|
Lysis buffer B |
1 mL×1 |
RT |
|
Beads |
0.8 mg×1 |
4℃ |
Protocol
The abundant serum protein depletion kit utilizes magnetic nanomaterials to enrich low-abundance proteins, enabling rapid and efficient preprocessing of serum samples. The entire workflow is straightforward and time-saving, making it suitable for various laboratory environments and experimental scales. As a magnetic bead-based kit, the following standardized protocol is recommended. Researchers may adjust the dilution ratio and incubation time according to specific experimental needs.
1. Sample Preprocessing
(1) Take an appropriate amount of fresh or thawed serum sample; a volume of 10-100 µL is recommended (depending on the kit size).
2. High-Abundance Protein Depletion
(1) Take an appropriate amount of pre-washed magnetic beads and add to the corresponding volume of serum sample.
(2) Mix thoroughly and incubate on a rotator for 10-15 minutes.
(3) Place the tube on a magnetic stand to separate the beads, and wash the beads to remove unbound components.
(4) Elute the low-abundance proteins from the magnetic beads.
3. Sample Concentration (Optional)
(1) If further concentration or buffer exchange is needed, use ultrafiltration tubes to process the collected sample.
4. Sample Storage and Application
(1) Immediate use: The protein sample after high-abundance protein depletion can be directly used in SDS-PAGE, Western blot, ELISA, LC-MS/MS, and other downstream applications.
(2) Storage: If not used immediately, aliquot and store at -80°C to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles and prevent protein degradation.
Figures
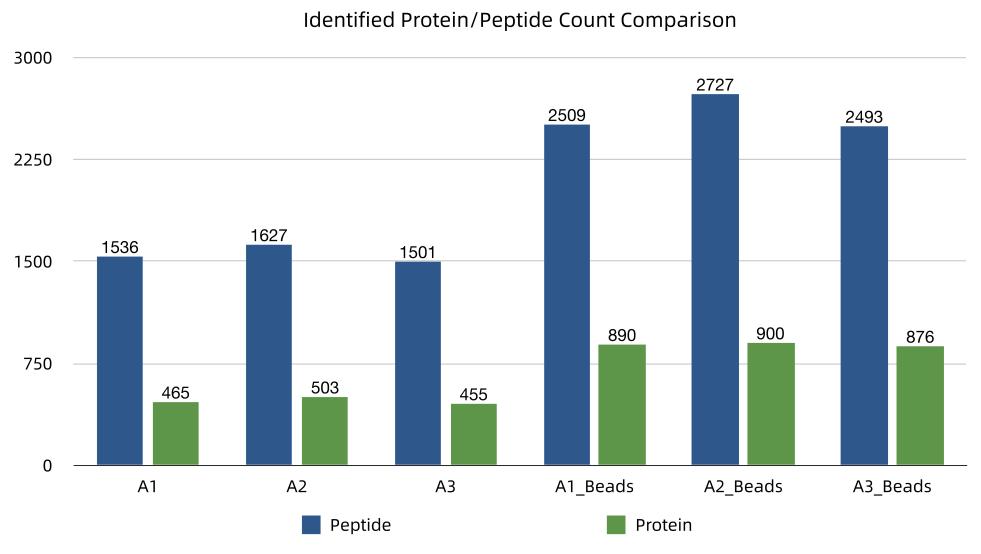
Figure 2. Experimental Renderings of Abundant Serum Protein Depletion Kit.
Features and Benefits
1. High Depletion Efficiency
Specifically adsorbs major high-abundance proteins in serum, with an average removal efficiency of 80-95%. This significantly reduces sample complexity and greatly enhances the signal intensity and detection depth of low-abundance proteins.
2. Minimal Protein Loss
Utilizes a mild buffer system to maximally preserve the structure and functionality of low-abundance proteins, making it suitable for downstream modification analysis and functional studies.
3. Simple Operation
No large-scale instruments required. The entire procedure can be completed in approximately 30-40 minutes with simple steps, ideal for routine laboratory workflows and improving experimental throughput.
4. Broad Compatibility
Compatible with a variety of downstream analytical techniques, including mass spectrometry, Western blotting, ELISA, and antibody validation, with no need for additional processing steps, greatly streamlining the experimental workflow.
5. Wide Applicability
Compatible with serum samples from humans, mice, rats, and other mammals. Suitable for diverse application scenarios in basic research, translational medicine, and animal model studies.
Applications
1. Serum Proteomics Research
By removing interfering proteins from serum, the overall sample complexity is significantly reduced, thereby enhancing LC-MS/MS detection depth in serum samples and enabling the discovery of key low-abundance regulatory proteins.
2. Biomarker Discovery
After depleting high-abundance proteins, changes in the expression of low-abundance differential proteins become more discernible, facilitating the identification of candidate biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis assessment in conditions such as cancer and metabolic diseases.
3. Post-Translational Modification (PTM) Studies
By minimizing interference from high-abundance proteins during enrichment and mass spectrometry detection, the abundant serum protein depletion kit allows for more accurate analysis of modifications such as phosphorylation, acetylation, and glycosylation.
4. Standardized Preprocessing of Clinical Samples
Through standardized analysis of serum samples from different patients, it helps to normalize sample backgrounds, improving the comparability and consistency of multi-sample data and supporting downstream statistical analysis.
FAQs
Q1: Is the Kit Compatible with Animal Serum Samples?
A1: Yes. In addition to human serum, the abundant serum protein depletion kit is also suitable for serum samples from mammals such as mice, rats, and rabbits. For other species or custom requirements, please contact MtoZ Biolabs technical support.
Q2: Can the Processed Samples Be Directly Analyzed by Mass Spectrometry?
A2: Yes. Samples treated with the kit require no additional steps and are ready for downstream applications such as LC-MS/MS, SDS-PAGE, Western Blot, and ELISA.
Q3: Will Low-Abundance Proteins Be Lost during Use?
A3: The abundant serum protein depletion kit utilizes highly selective affinity matrices and a gentle buffer system to minimize non-specific adsorption, ensuring maximum retention of low-abundance proteins and their post-translational modifications, it is an ideal choice for mass spectrometry and functional studies.
Q4: What Is the Maximum Sample Volume that Can Be Processed?
A4: The standard kit supports 10-100μL of serum per reaction. Multiple package sizes are available to accommodate different experimental scales.
Q5: Is the sample processing workflow complex? Does it require special equipment?
A5: The workflow is simple and can be completed within 30-40 minutes. Only a magnetic rack is required, with no need for large-scale instruments, making it suitable for routine laboratory conditions.







