Optimized Strategies for Processing Membrane Proteins via FASP or In-Gel Digestion
-
High hydrophobicity: Poor solubility in aqueous buffers and a tendency to form aggregates
-
Low abundance: Represent a small fraction of the total proteome, especially in the case of multi-pass membrane proteins
-
Susceptibility to loss or denaturation: Prone to degradation or precipitation during extraction and digestion processes
-
Lipid contamination: Frequently associated with lipid interference, which compromises enzymatic digestion efficiency and MS performance
-
Efficient removal of contaminants: Repeated buffer exchange through the filter removes residual denaturants such as SDS and urea, preventing MS interference.
-
Minimized precipitation: Membrane proteins are immobilized on the filter, avoiding precipitation during digestion due to hydrophobicity.
-
Suitable for low-abundance samples: Enables effective processing of limited or dilute membrane protein preparations, such as tissue or cell membrane fractions.
-
Membrane protein extracts containing high concentrations of strong denaturants such as SDS
-
Low-abundance or poorly soluble membrane protein mixtures
-
Proteomics workflows where gel-based staining or separation is undesirable
-
Protein solubilization: Use Laemmli buffer or lysis buffer containing 1% SDS to improve loading of membrane proteins;
-
Staining method: Apply MS-compatible dyes such as Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250;
-
De-staining protocol: Avoid excessive acetonitrile concentrations to minimize peptide loss;
-
Dual-enzyme strategy: Combine Lys-C and trypsin to improve digestion efficiency, especially within transmembrane domains;
-
Digestion duration: Extend incubation time to enhance recovery of hydrophobic peptides.
-
Targeted enrichment of specific membrane proteins such as ion channels or receptors;
-
Comparative analysis of post-translationally modified isoforms;
-
Studies involving membrane protein expression constructs or purified samples.
-
Compatibility with diverse lysis buffers and FASP/in-gel workflows
-
Optimized dual-enzyme digestion to enhance detection of transmembrane domains
-
Automated sample preparation platforms to minimize manual variability
-
Support for integrative analyses including quantitative proteomics and multi-modification studies (e.g., phosphorylation, glycosylation)
Due to their intrinsic properties, high hydrophobicity, low solubility, and strong tendency to aggregate, membrane proteins have long posed technical challenges in proteomics. Efficient extraction, enzymatic digestion, and mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of membrane proteins depend heavily on the selection of appropriate sample preparation strategies. Among the commonly adopted digestion methods, Filter-Aided Sample Preparation (FASP) and in-gel digestion are applicable to membrane protein processing but require specific optimization to address their unique biochemical characteristics.
Challenges of Membrane Proteins: Why Are They Difficult to Digest?
Membrane proteins are typically embedded within cellular membranes and contain multiple transmembrane domains. Their physicochemical properties include:
As such, sample preparation workflows for membrane proteins must achieve efficient removal of interfering substances (e.g., detergents, lipids), enhance solubilization and enzymatic accessibility, and maintain compatibility with downstream MS analysis.
Filter-Aided Sample Preparation (FASP): An Efficient Workflow for Membrane Proteins
1. Principle
Originally introduced by Wisniewski et al. in 2009, the FASP method utilizes ultrafiltration devices (typically with 10 or 30 kDa molecular weight cut-offs) to denature and retain proteins on a filter membrane. The entire sequence of buffer exchange, reduction, alkylation, and enzymatic digestion is performed on the membrane, minimizing sample loss and contamination.
2. Advantages for Membrane Protein Processing
3. Optimization Recommendations

4. Recommended Applications
In-Gel Digestion: A Classical Method Combining Enrichment and Resolution
1. Principle
In-gel digestion involves separating membrane proteins by SDS-PAGE, excising the desired protein bands or regions, and conducting de-staining, reduction, alkylation, and enzymatic digestion within the gel matrix. The resulting peptides are extracted and concentrated prior to MS analysis.
2. Strengths and Limitations

3. Optimization Recommendations for Membrane Proteins
4. Recommended Applications
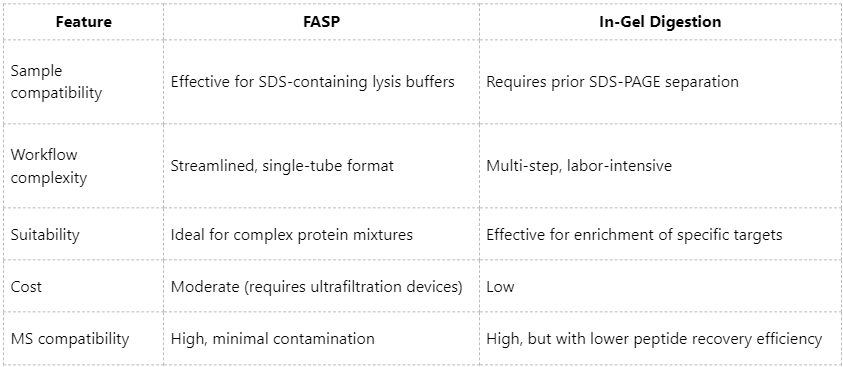
Comparative Summary of Sample Preparation Methods for Membrane Proteins
MtoZ Biolabs' Membrane Proteomics Solutions
In membrane proteomics, integrating standardized sample preparation workflows with high-sensitivity MS platforms is essential for reliable data acquisition. MtoZ Biolabs has developed a dedicated membrane protein analysis pipeline leveraging the advanced Orbitrap Exploris 480 system and optimized enzymatic protocols, including:
With extensive experience in studying GPCRs, transporters, and membrane receptors, MtoZ Biolabs delivers robust data support for functional characterization and drug target discovery.
The inherent resistance of membrane proteins to enzymatic digestion should not hinder proteomics research. By adopting scientifically validated workflows such as FASP or in-gel digestion, coupled with optimized digestion conditions and high-resolution MS, researchers can achieve comprehensive, high-sensitivity profiling of membrane proteins. If you face challenges in membrane protein studies, MtoZ Biolabs offers customized proteomics solutions to accelerate your scientific breakthroughs.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







